
What is Lean Six Sigma?
• Lean and Six Sigma are both process improvement methodologies
• Lean is about speed and efficiency
• Six Sigma is about precision and accuracy ¨C leading to data-driven decisions
• Both rooted in the 1980s (and earlier)
Lean arose as a method to optimize auto manufacturing
Six Sigma evolved as a quality initiative to reduce variance in the semiconductor industry
Why Lean and Six Sigma?
• Six Sigma will eliminate defects but it will not address the question of how to optimize process flow
• Lean principles exclude the advanced statistical tools often required to achieve the process capabilities needed to be truly 'lean?
• Each approach can result in dramatic improvement, while utilizing both methods simultaneously holds the promise of being able to address all types of process problems with the most appropriate toolkit.
For example, inventory reduction not only requires reducing batch sizes and linking operations by using Lean, but also minimizing process variation by utilizing Six Sigma tools.
Lean Six Sigma Goals and Benefits
• Achieve total customer satisfaction and improved operational effectiveness and efficiency
Remove wasteful/non-value added activities
Decrease defects and cycle time, and increase first pass yields
• Improve communication and teamwork through a common set of tools and techniques (a disciplined, repeatable methodology)
• Develop leaders in breakthrough technologies to meet stretch goals of producing better products and services delivered faster and at lower cost
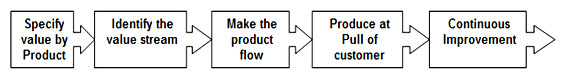
Lean Principles
• Specify value by product: Identify customer needs, specifications and requirements
• Identify the value stream: Identify the process from product design to sales and to satisfying the customer¡¯s needs and eliminate waste / variation
• Make the product flow: Identify the bottlenecks within the process
• Produce at the Pull of customer: Make the products to meet customer¡¯s needs and requirements, and make it available when the customer wants it
• In pursuit of perfection (Continuous Improvement)
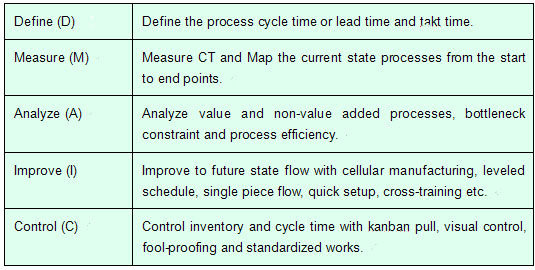
Lean Six Sigma DMAIC
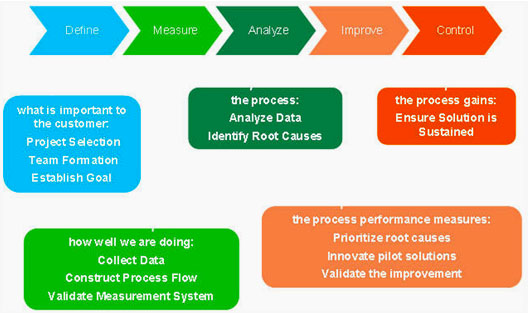
Lean Six Sigma Principles
• Continually focus on value for all stakeholders
• Optimize enterprise flow
• Optimize process capabilities
• Assure seamless flow of information
• Use flexible, pull processes
• Enable visual controls
• Have all tools & information at the point-of-use
• Apply standard methods & mistake proofing
• Build relationships across the value chain
Lean Six Sigma Tools

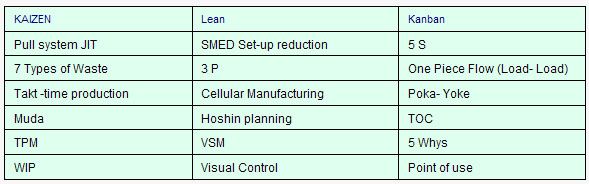
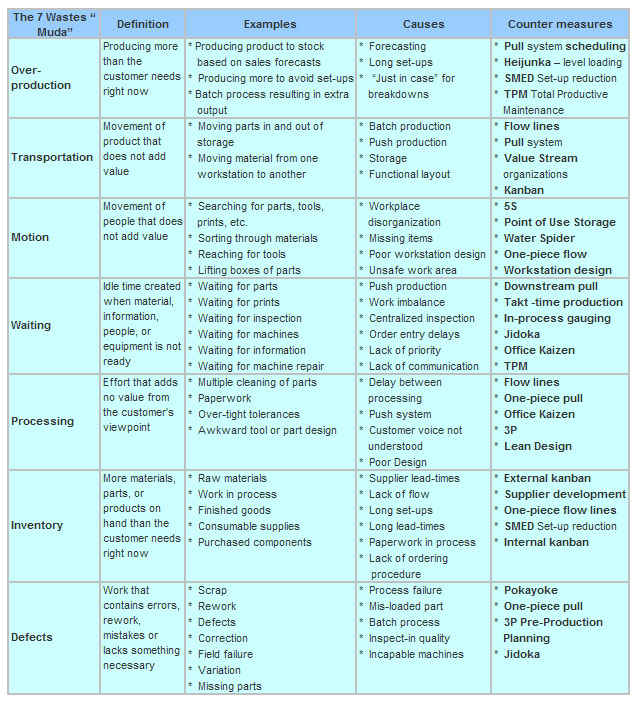
Roadmap to eliminate the Seven Production Wastes
» More Information 
