
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
ISO/TS16949
Third edition
2009-06-15
Quality management systems
¡ª Particular requirements for the application of ISO 9001:2008 for automotive production and relevant service part organizations
Reference number
ISO/TS 16949:2009(E)
© ISO 2009
Introduction
0.1 General
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
Introduction
0.1 General
The adoption of a quality management system should be a strategic decision of an organization. The design and
implementation of an organization's quality management system is influenced by
a) its organizational environment, changes in that environment, and the risks associated with that environment,
b) its varying needs,
c) its particular objectives,
d) the products it provides,
e) the processes it employs,
f) its size and organizational structure.
It is not the intent of this International Standard to imply uniformity in the structure of quality management systems or uniformity of documentation.
The quality management system requirements specified in this International Standard are complementary to requirements for products. Information marked ¡°NOTE¡± is for guidance in understanding or clarifying the associated requirement.
This International Standard can be used by internal and external parties, including certification bodies, to assess the organization's ability to meet customer, statutory and regulatory requirements applicable to the product, and the organization's own requirements.
The quality management principles stated in ISO 9000 and ISO 9004 have been taken into consideration during the development of this International Standard.
0.2 Process approach
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
0.2 Process approach
This International Standard promotes the adoption of a process approach when developing, implementing and improving the effectiveness of a quality management system, to enhance customer satisfaction by meeting customer requirements.
For an organization to function effectively, it has to determine and manage numerous linked activities. An activity or set of activities using resources, and managed in order to enable the transformation of inputs into outputs, can be considered as a process. Often the output from one process directly forms the input to the next.
The application of a system of processes within an organization, together with the identification and interactions of these processes, and their management to produce the desired outcome, can be referred to as the ¡°process approach¡±.
An advantage of the process approach is the ongoing control that it provides over the linkage between the individual processes within the system of processes, as well as over their combination and interaction.
When used within a quality management system, such an approach emphasizes the importance of
a) understanding and meeting requirements,
b) the need to consider processes in terms of added value,
c) obtaining results of process performance and effectiveness, and
d) continual improvement of processes based on objective measurement.
The model of a process-based quality management system shown in Figure 1 illustrates the process linkages presented in Clauses 4 to 8. This illustration shows that customers play a significant role in defining requirements as inputs. Monitoring of customer satisfaction requires the evaluation of information relating to customer perception as to whether the organization has met the customer requirements. The model shown in Figure 1 covers all the requirements of this International Standard, but does not show processes at a detailed level.
NOTE In addition, the methodology known as ¡°Plan-Do-Check-Act¡± (PDCA ) can be applied to all processes.
PDCA can be briefly described as follows.
Plan: establish the objectives and processes necessary to deliver results in accordance with customer requirements and the organization's policies.
Do: implement the processes.
Check: monitor and measure processes and product against policies, objectives and requirements for the product and
report the results.
Act: take actions to continually improve process performance.
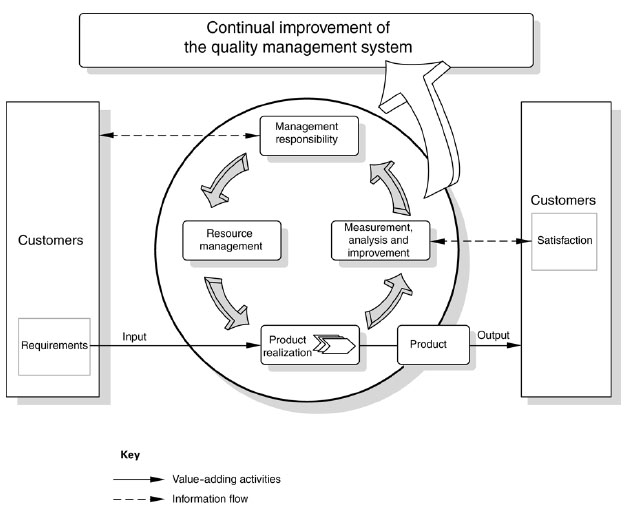
Figure 1 ¡ª Model of a process-based quality management system
0.3 Relationship with ISO 9004
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
0.3 Relationship with ISO 9004
ISO 9001 and ISO 9004 are quality management system standards which have been designed to complement each other, but can also be used independently.
ISO 9001 specifies requirements for a quality management system that can be used for internal application by organizations, or for certification, or for contractual purposes. It focuses on the effectiveness of the quality management system in meeting customer requirements.
At the time of publication of this International Standard, ISO 9004 is under revision. The revised edition of ISO 9004 will provide guidance to management for achieving sustained success for any organization in a complex, demanding, and ever changing, environment. ISO 9004 provides a wider focus on quality management than ISO 9001; it addresses the needs and expectations of all interested parties and their satisfaction, by the systematic and continual improvement of the organization¡¯s performance.
However, it is not intended for certification, regulatory or contractual use.
NOTE The knowledge and use of the eight quality management principles referred to in ISO 9000:2005 and ISO 9004 ¡ª should be demonstrated and cascaded through the organization by top management.
0.4 Compatibility with other management systems
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
0.4 Compatibility with other management systems
During the development of this International Standard, due consideration was given to the provisions of ISO 14001:2004 to enhance the compatibility of the two standards for the benefit of the user community. Annex A shows the correspondence between ISO 9001:2008 and ISO 14001:2004.
This International Standard does not include requirements specific to other management systems, such as those
particular to environmental management, occupational health and safety management, financial management or risk management. However, this International Standard enables an organization to align or integrate its own quality management system with related management system requirements. It is possible for an organization to adapt its existing management system(s) in order to establish a quality management system that complies with the requirements of this International Standard.
0.5 Goal of this Technical Specification
The goal of this Technical Specification is the development of a quality management system that provides for continual improvement, emphasizing defect prevention and the reduction of variation and waste in the supply chain.
This Technical Specification, coupled with applicable customer-specific requirements, defines the fundamental quality management system requirements for those subscribing to this Technical Specification.
This Technical Specification is intended to avoid multiple certification audits and provide a common approach to a quality management system for automotive production, and relevant service part organizations.
Quality management systems
¡ª Particular requirements for the application of ISO 9001:2008 for automotive production and relevant service part organizations
1 Scope
1.1 General
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
1 Scope
1.1 General
This International Standard specifies requirements for a quality management system where an organization
a) needs to demonstrate its ability to consistently provide product that meets customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements, and
b) aims to enhance customer satisfaction through the effective application of the system, including processes for continual improvement of the system and the assurance of conformity to customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements.
NOTE 1 In this International Standard, the term ¡°product¡± only applies to
a) product intended for, or required by, a customer,
b) any intended output resulting from the product realization processes.
NOTE 2 Statutory and regulatory requirements can be expressed as legal requirements.
This Technical Specification, in conjunction with ISO 9001:2008, defines the quality management system requirements for the design and development, production and, when relevant, installation and service of automotive-related products.
This Technical Specification is applicable to sites of the organization where customer-specified parts, for production and/or service, are manufactured.
Supporting functions, whether on-site or remote (such as design centres, corporate headquarters and distribution centres), form part of the site audit as they support the site, but cannot obtain stand-alone certification to this Technical Specification.
This Technical Specification can be applied throughout the automotive supply chain.
1.2 Application
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
1.2 Application
All requirements of this International Standard are generic and are intended to be applicable to all organizations, regardless of type, size and product provided.
Where any requirement(s) of this International Standard cannot be applied due to the nature of an organization and its product, this can be considered for exclusion.
Where exclusions are made, claims of conformity to this International Standard are not acceptable unless these exclusions are limited to requirements within Clause 7, and such exclusions do not affect the organization's ability, or responsibility, to provide product that meets customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements.
The only permitted exclusions for this Technical Specification relate to 7.3 where the organization is not responsible for product design and development.
Permitted exclusions do not include manufacturing process design.
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this document.
For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO 9000:2005, Quality management systems ¡ª Fundamentals and vocabulary
3 Terms and definitions
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in ISO 9000 apply.
Throughout the text of this International Standard, wherever the term ¡°product¡± occurs, it can also mean ¡°service¡±.
3.1 Terms and definitions for the automotive industry
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in ISO 9000:2005 and the following apply.
3.1.1
control plan
documented description of the systems and processes required for controlling product
NOTE See Annex A.
3.1.2
design responsible organization
organization with authority to establish a new, or change an existing, product specification
NOTE This responsibility includes testing and verification of design performance within the customer's specified
application.
3.1.3
error proofing
product and manufacturing process design and development to prevent manufacture of nonconforming products
3.1.4
laboratory
facility for inspection, test or calibration that may include, but is not limited to, chemical, metallurgical, dimensional, physical, electrical or reliability testing
3.1.5
laboratory scope
controlled document containing
•specific tests, evaluations and calibrations that a laboratory is qualified to perform,
•a list of the equipment which it uses to perform the above, and
•a list of methods and standards to which it performs the above
3.1.6
manufacturing
process of making or fabricating
•production materials,
•production or service parts,
•assemblies, or
•heat treating, welding, painting, plating or other finishing services
3.1.7
predictive maintenance
activities based on process data aimed at the avoidance of maintenance problems by prediction of likely failure modes
3.1.8
preventive maintenance
planned action to eliminate causes of equipment failure and unscheduled interruptions to production, as an output of the manufacturing process design
3.1.9
premium freight
extra costs or charges incurred additional to contracted delivery
NOTE This can be caused by method, quantity, unscheduled or late deliveries, etc.
3.1.10
remote location
location that supports sites and at which non-production processes occur
3.1.11
site
location at which value-added manufacturing processes occur
3.1.12
special characteristic
product characteristic or manufacturing process parameter which can affect safety or compliance with regulations, fit, function, performance or subsequent processing of product
4 Quality management system
4.1 General requirements
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
4 Quality management system
4.1 General requirements
The organization shall establish, document, implement and maintain a quality management system and continually improve its effectiveness in accordance with the requirements of this International Standard.
The organization shall
a) determine the processes needed for the quality management system and their application throughout the
organization (see 1.2),
b) determine the sequence and interaction of these processes,
c) determine criteria and methods needed to ensure that both the operation and control of these processes are effective,
d) ensure the availability of resources and information necessary to support the operation and monitoring of these processes,
e) monitor, measure where applicable, and analyse these processes, and
f) implement actions necessary to achieve planned results and continual improvement of these processes.
These processes shall be managed by the organization in accordance with the requirements of this International Standard.
Where an organization chooses to outsource any process that affects product conformity to requirements, the organization shall ensure control over such processes. The type and extent of control to be applied to these outsourced processes shall be defined within the quality management system.
NOTE 1 Processes needed for the quality management system referred to above should include processes for management activities, provision of resources, product realization, measurement, analysis and improvement.
NOTE 2 An ¡°outsourced process¡± is a process that the organization needs for its quality management system and which the organization chooses to have performed by an external party.
NOTE 3 Ensuring control over outsourced processes does not absolve the organization of the responsibility of conformity to all customer, statutory and regulatory requirements. The type and extent of control to be applied to the outsourced process can be influenced by factors such as
a) the potential impact of the outsourced process on the organization's capability to provide product that conforms to requirements,
b) the degree to which the control for the process is shared,
c) the capability of achieving the necessary control through the application of 7.4.
4.1.1 General requirements ¡ª Supplemental
Ensuring control over outsourced processes shall not absolve the organization of the responsibility of conformity to all customer requirements.
NOTE See also 7.4.1 and 7.4.1.3.
4.2 Documentation requirements
4.2.1 General
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
4.2 Documentation requirements
4.2.1 General
The quality management system documentation shall include
a) documented statements of a quality policy and quality objectives,
b) a quality manual,
c) documented procedures and records required by this International Standard, and
d) documents, including records, determined by the organization to be necessary to ensure the effective planning, operation and control of its processes.
NOTE 1 Where the term ¡°documented procedure¡± appears within this International Standard, this means that the procedure is established, documented, implemented and maintained. A single document may address the requirements for one or more procedures. A requirement for a documented procedure may be covered by more than one document.
NOTE 2 The extent of the quality management system documentation can differ from one organization to another due to
a) the size of organization and type of activities,
b) the complexity of processes and their interactions, and
c) the competence of personnel.
NOTE 3 The documentation can be in any form or type of medium.
4.2.2 Quality manual
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
4.2.2 Quality manual
The organization shall establish and maintain a quality manual that includes
a) the scope of the quality management system, including details of and justification for any exclusions (see 1.2),
b) the documented procedures established for the quality management system, or reference to them, and
c) a description of the interaction between the processes of the quality management system.
4.2.3 Control of documents
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
4.2.3 Control of documents
Documents required by the quality management system shall be controlled. Records are a special type of
document and shall be controlled according to the requirements given in 4.2.4.
A documented procedure shall be established to define the controls needed
a) to approve documents for adequacy prior to issue,
b) to review and update as necessary and re-approve documents,
c) to ensure that changes and the current revision status of documents are identified,
d) to ensure that relevant versions of applicable documents are available at points of use,
e) to ensure that documents remain legible and readily identifiable,
f) to ensure that documents of external origin determined by the organization to be necessary for the planning and
operation of the quality management system are identified and their distribution controlled, and
g) to prevent the unintended use of obsolete documents, and to apply suitable identification to them if they are
retained for any purpose.
4.2.3.1 Engineering specifications
The organization shall have a process to assure the timely review, distribution and implementation of all customer engineering standards/specifications and changes based on customer-required schedule. Timely review should be as soon as possible, and shall not exceed two working weeks.
The organization shall maintain a record of the date on which each change is implemented in production. Implementation shall include updated documents.
NOTE A change in these standards/specifications requires an updated record of customer production part approval
when these specifications are referenced on the design record or if they affect documents of production part approval process, such as control plan, FMEAs, etc.
4.2.4 Control of records
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
4.2.4 Control of records
Records established to provide evidence of conformity to requirements and of the effective operation of the
quality management system shall be controlled.
The organization shall establish a documented procedure to define the controls needed for the identification, storage, protection, retrieval, retention and disposition of records.
Records shall remain legible, readily identifiable and retrievable.
NOTE 1 ¡°Disposition¡± includes disposal.
NOTE 2 ¡°Records¡± also include customer-specified records.
4.2.4.1 Records retention
The control of records shall satisfy statutory, regulatory and customer requirements.
5 Management responsibility
5.1 Management commitment
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5 Management responsibility
5.1 Management commitment
Top management shall provide evidence of its commitment to the development and implementation of the quality
management system and continually improving its effectiveness by
a) communicating to the organization the importance of meeting customer as well as statutory and regulatory requirements,
b) establishing the quality policy,
c) ensuring that quality objectives are established,
d) conducting management reviews, and
e) ensuring the availability of resources.
5.1.1 Process efficiency
Top management shall review the product realization processes and the support processes to assure their effectiveness and efficiency.
5.2 Customer focus
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.2 Customer focus
Top management shall ensure that customer requirements are determined and are met with the aim of enhancing customer satisfaction (see 7.2.1 and 8.2.1).
5.3 Quality policy
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.3 Quality policy
Top management shall ensure that the quality policy
a) is appropriate to the purpose of the organization,
b) includes a commitment to comply with requirements and continually improve the effectiveness of the quality management system,
c) provides a framework for establishing and reviewing quality objectives,
d) is communicated and understood within the organization, and
e) is reviewed for continuing suitability.
5.4 Planning
5.4.1 Quality objectives
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.4 Planning
5.4.1 Quality objectives
Top management shall ensure that quality objectives, including those needed to meet requirements for product
[see 7.1 a)], are established at relevant functions and levels within the organization. The quality objectives shall be measurable and consistent with the quality policy.
5.4.1.1 Quality objectives ¡ª Supplemental
Top management shall define quality objectives and measurements that shall be included in the business plan and used to deploy the quality policy.
NOTE Quality objectives should address customer expectations and be achievable within a defined time period.
5.4.2 Quality management system planning
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.4.2 Quality management system planning
Top management shall ensure that
a) the planning of the quality management system is carried out in order to meet the requirements given in
4.1, as well as the quality objectives, and
b) the integrity of the quality management system is maintained when changes to the quality management system are planned and implemented.
5.5 Responsibility, authority and communication
5.5.1 Responsibility and authority
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.5 Responsibility, authority and communication
5.5.1 Responsibility and authority
Top management shall ensure that responsibilities and authorities are defined and communicated within the organization.
5.5.1.1 Responsibility for quality
Managers with responsibility and authority for corrective action shall be promptly informed of products or processes which do not conform to requirements.
Personnel responsible for conformity to product requirements shall have the authority to stop production to correct quality problems.
Production operations across all shifts shall be staffed with personnel in charge of, or delegated responsibility for,ensuring conformity to product requirements.
5.5.2 Management representative
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.5.2 Management representative
Top management shall appoint a member of the organization's management who, irrespective of other responsibilities, shall have responsibility and authority that includes
a) ensuring that processes needed for the quality management system are established, implemented and maintained,
b) reporting to top management on the performance of the quality management system and any need for improvement, and
c) ensuring the promotion of awareness of customer requirements throughout the organization.
NOTE The responsibility of a management representative can include liaison with external parties on matters relating
to the quality management system.
5.5.2.1 Customer representative
Top management shall designate personnel with responsibility and authority to ensure that customer requirements are addressed. This includes selection of special characteristics, setting quality objectives and related training, corrective and preventive actions, product design and development.
5.5.3 Internal communication
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.5.3 Internal communication
Top management shall ensure that appropriate communication processes are established within the organization and that communication takes place regarding the effectiveness of the quality management system.
5.6 Management review
5.6.1 General
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.6 Management review
5.6.1 General
Top management shall review the organization's quality management system, at planned intervals, to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy and effectiveness. This review shall include assessing opportunities for improvement and the need for changes to the quality management system, including the quality policy and quality objectives.
Records from management reviews shall be maintained (see 4.2.4).
5.6.1.1 Quality management system performance
These reviews shall include all requirements of the quality management system and its performance trends as an essential part of the continual improvement process.
Part of the management review shall be the monitoring of quality objectives, and the regular reporting and evaluation of the cost of poor quality (see 8.4.1 and 8.5.1).
These results shall be recorded to provide, as a minimum, evidence of the achievement of
--- the quality objectives specified in the business plan, and
--- customer satisfaction with product supplied.
5.6.2 Review input
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.6.2 Review input
The input to management review shall include information on
a) results of audits,
b) customer feedback,
c) process performance and product conformity,
d) status of preventive and corrective actions,
e) follow-up actions from previous management reviews,
f) changes that could affect the quality management system, and
g) recommendations for improvement.
5.6.2.1 Review input ¡ª Supplemental
Input to management review shall include an analysis of actual and potential field-failures and their impact on quality, safety or the environment.
5.6.3 Review output
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
5.6.3 Review output
The output from the management review shall include any decisions and actions related to
a) improvement of the effectiveness of the quality management system and its processes,
b) improvement of product related to customer requirements, and
c) resource needs.
6 Resource management
6.1 Provision of resources
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
6 Resource management
6.1 Provision of resources
The organization shall determine and provide the resources needed
a) to implement and maintain the quality management system and continually improve its effectiveness, and
b) to enhance customer satisfaction by meeting customer requirements.
6.2 Human resources
6.2.1 General
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
6.2 Human resources
6.2.1 General
Personnel performing work affecting conformity to product requirements shall be competent on the basis of appropriate education, training, skills and experience.
NOTE Conformity to product requirements can be affected directly or indirectly by personnel performing any task within the quality management system.
6.2.2 Competence, training and awareness
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
6.2.2 Competence, training and awareness
The organization shall
a) determine the necessary competence for personnel performing work affecting conformity to product requirements,
b) where applicable, provide training or take other actions to achieve the necessary competence,
c) evaluate the effectiveness of the actions taken,
d) ensure that its personnel are aware of the relevance and importance of their activities and how they contribute to the achievement of the quality objectives, and
e) maintain appropriate records of education, training, skills and experience (see 4.2.4).
6.2.2.1 Product design skills
The organization shall ensure that personnel with product design responsibility are competent to achieve design requirements and are skilled in applicable tools and techniques.
Applicable tools and techniques shall be identified by the organization.
6.2.2.2 Training
The organization shall establish and maintain documented procedures for identifying training needs and achieving competence of all personnel performing activities affecting conformity to product requirements. Personnel performing specific assigned tasks shall be qualified, as required,
with particular attention to the satisfaction of customer requirements.
NOTE 1 This applies to all employees having an effect on quality at all levels of the organization.
NOTE 2 An example of the customer-specific requirements is the application of digitized mathematically based data.
6.2.2.3 Training on the job
The organization shall provide on-the-job training for personnel in any new or modified job affecting conformity to product requirements, including contract or agency personnel. Personnel whose work can affect quality shall be informed about the consequences to the customer of nonconformity to quality requirements.
6.2.2.4 Employee motivation and empowerment
The organization shall have a process to motivate employees to achieve quality objectives, to make continual
improvements, and to create an environment to promote innovation. The process shall include the promotion of quality and technological awareness throughout the whole organization.
The organization shall have a process to measure the extent to which its personnel are aware of the relevance and importance of their activities and how they contribute to the achievement of the quality objectives [see 6.2.2 d)].
6.3 Infrastructure
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
6.3 Infrastructure
The organization shall determine, provide and maintain the infrastructure needed to achieve conformity to product requirements. Infrastructure includes, as applicable,
a) buildings, workspace and associated utilities,
b) process equipment (both hardware and software), and
c) supporting services (such as transport, communication or information systems).
6.3.1 Plant, facility and equipment planning
The organization shall use a multidisciplinary approach (see 7.3.1.1) for developing plant, facility and equipment plans. Plant layouts shall optimize material travel, handling and value-added use of floor space, and shall facilitate synchronous material flow. Methods shall be developed and implemented to evaluate and monitor the effectiveness of existing operations.
NOTE These requirements should focus on lean manufacturing principles and the link to the effectiveness of the quality management system.
6.3.2 Contingency plans
The organization shall prepare contingency plans to satisfy customer requirements in the event of an emergency such as utility interruptions, labour shortages, key equipment failure and field returns.
6.4 Work environment
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
6.4 Work environment
The organization shall determine and manage the work environment needed to achieve conformity to product requirements.
NOTE The term ¡°work environment¡± relates to those conditions under which work is performed including physical, environmental and other factors (such as noise, temperature, humidity, lighting or weather).
6.4.1 Personnel safety to achieve conformity to product requirements
Product safety and means to minimize potential risks to employees shall be addressed by the organization, especially in the design and development process and in manufacturing process activities.
6.4.2 Cleanliness of premises
The organization shall maintain its premises in a state of order, cleanliness and repair consistent with the product and manufacturing process needs.
7 Product realization
7.1 Planning of product realization
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7 Product realization
7.1 Planning of product realization
The organization shall plan and develop the processes needed for product realization. Planning of product realization shall be consistent with the requirements of the other processes of the quality management system (see 4.1).
In planning product realization, the organization shall determine the following, as appropriate:
a) quality objectives and requirements for the product;
b) the need to establish processes and documents, and to provide resources specific to the product;
c) required verification, validation, monitoring, measurement, inspection and test activities specific to the product and the criteria for product acceptance;
d) records needed to provide evidence that the realization processes and resulting product meet requirements (see 4.2.4).
The output of this planning shall be in a form suitable for the organization's method of operations.
NOTE 1 A document specifying the processes of the quality management system (including the product realization processes) and the resources to be applied to a specific product, project or contract can be referred to as a quality plan.
NOTE 2 The organization may also apply the requirements given in 7.3 to the development of product realization processes.
NOTE Some customers refer to project management or advanced product quality planning as a means to achieve
product realization. Advanced product quality planning embodies the concepts of error prevention and continual improvement as contrasted with error detection, and is based on a multidisciplinary approach.
7.1.1 Planning of product realization ¡ª Supplemental
Customer requirements and references to its technical specifications shall be included in the planning of product realization as a component of the quality plan.
7.1.2 Acceptance criteria
Acceptance criteria shall be defined by the organization and, where required, approved by the customer.
For attribute data sampling, the acceptance level shall be zero defects (see 8.2.3.1).
7.1.3 Confidentiality
The organization shall ensure the confidentiality of customer-contracted products and projects under development, and related product information.
7.1.4 Change control
The organization shall have a process to control and react to changes that impact product realization. The effects of any change, including those changes caused by any supplier, shall be assessed, and verification and validation activities shall be defined, to ensure compliance with customer requirements. Changes shall be validated before implementation.
For proprietary designs, impact on form, fit and function (including performance and/or durability) shall be reviewed with the customer so that all effects can be properly evaluated.
When required by the customer, additional verification/identification requirements, such as those required for new product introduction, shall be met.
NOTE 1 Any product realization change affecting customer requirements requires notification to, and agreement from,
the customer.
NOTE 2 The above requirement applies to product and manufacturing process changes.
7.2 Customer-related processes
7.2.1 Determination of requirements related to the product
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.2Customer-related processes
7.2.1 Determination of requirements related to the product
The organization shall determine
a) requirements specified by the customer, including the requirements for delivery and post-delivery activities,
b) requirements not stated by the customer but necessary for specified or intended use, where known,
c) statutory and regulatory requirements applicable to the product, and
d) any additional requirements considered necessary by the organization.
NOTE Post-delivery activities include, for example, actions under warranty provisions, contractual obligations such as
maintenance services, and supplementary services such as recycling or final disposal.
NOTE 1 Post-delivery activities include any after-sales product service provided as part of the customer contract or
purchase order.
NOTE 2 This requirement includes recycling, environmental impact and characteristics identified as a result of the organization's knowledge of the product and manufacturing processes (see 7.3.2.3).
NOTE 3 Compliance to item c) includes all applicable government, safety and environmental regulations, applied to
acquisition, storage, handling, recycling, elimination or disposal of materials.
7.2.1.1 Customer-designated special characteristics
The organization shall demonstrate conformity to customer requirements for designation, documentation and control of special characteristics.
7.2.2 Review of requirements related to the product
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.2.2 Review of requirements related to the product
The organization shall review the requirements related to the product. This review shall be conducted prior to the organization's commitment to supply a product to the customer (e.g. submission of tenders, acceptance of contracts or orders, acceptance of changes to contracts or orders) and shall ensure that
a) product requirements are defined,
b) contract or order requirements differing from those previously expressed are resolved, and
c) the organization has the ability to meet the defined requirements.
Records of the results of the review and actions arising from the review shall be maintained (see 4.2.4).
Where the customer provides no documented statement of requirement, the customer requirements shall be confirmed by the organization before acceptance.
Where product requirements are changed, the organization shall ensure that relevant documents are amended and that relevant personnel are made aware of the changed requirements.
NOTE In some situations, such as internet sales, a formal review is impractical for each order. Instead the review can
cover relevant product information such as catalogues or advertising material.
7.2.2.1 Review of requirements related to the product ¡ª Supplemental
Waiving the requirement stated in 7.2.2 for a formal review (see note) shall require customer authorization.
7.2.2.2 Organization manufacturing feasibility
The organization shall investigate, confirm and document the manufacturing feasibility of the proposed products in the contract review process, including risk analysis.
7.2.3 Customer communication
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.2.3 Customer communication
The organization shall determine and implement effective arrangements for communicating with customers in relation to
a) product information,
b) enquiries, contracts or order handling, including amendments, and
c) customer feedback, including customer complaints.
7.2.3.1 Customer communication ¡ª Supplemental
The organization shall have the ability to communicate necessary information, including data, in a customer-specified
language and format (e.g. computer-aided design data, electronic data exchange).
7.3 Design and development
NOTE The requirements of 7.3 include product and manufacturing process design and development, and focus on error prevention rather than detection.
7.3.1 Design and development planning
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.3Design and development
7.3.1 Design and development planning
The organization shall plan and control the design and development of product.
During the design and development planning, the organization shall determine
a) the design and development stages,
b) the review, verification and validation that are appropriate to each design and development stage, and
c) the responsibilities and authorities for design and development.
The organization shall manage the interfaces between different groups involved in design and development to ensure effective communication and clear assignment of responsibility.
Planning output shall be updated, as appropriate, as the design and development progresses.
NOTE Design and development review, verification and validation have distinct purposes. They can be conducted and
recorded separately or in any combination, as suitable for the product and the organization.
7.3.1.1 Multidisciplinary approach
•The organization shall use a multidisciplinary approach to prepare for product realization, including development/finalization and monitoring of special characteristics,
•development and review of FMEAs, including actions to reduce potential risks, and
•development and review of control plans.
NOTE A multidisciplinary approach typically includes the organization's design, manufacturing, engineering, quality, production and other appropriate personnel.
7.3.2 Design and development inputs
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.3.2 Design and development inputs
Inputs relating to product requirements shall be determined and records maintained (see 4.2.4).
These inputs shall include
a) functional and performance requirements,
b) applicable statutory and regulatory requirements,
c) where applicable, information derived from previous similar designs, and
d) other requirements essential for design and development.
The inputs shall be reviewed for adequacy. Requirements shall be complete, unambiguous and not in conflict with each other.
NOTE Special characteristics (see 7.2.1.1) are included in this requirement.
7.3.2.1 Product design input
The organization shall identify, document and review the product design input requirements, including the following:
•customer requirements (contract review) such as special characteristics (see 7.3.2.3), identification, traceability and packaging;
•use of information: the organization shall have a process to deploy information gained from previous design projects, competitor analysis, supplier feedback, internal input, field data, and other relevant sources, for current and future projects of a similar nature;
•targets for conformity to product requirements, life, reliability, durability, maintainability, timing and cost.
7.3.2.2 Manufacturing process design input
The organization shall identify, document and review the manufacturing process design input requirements, including
•product design output data,
•targets for productivity, process capability and cost, customers requirements, if any, and
•experience from previous developments.
NOTE The manufacturing process design includes the use of error-proofing methods to a degree appropriate to the magnitude of the problems and commensurate with the risks encountered.
7.3.2.3 Special characteristics
• The organization shall identify special characteristics [see 7.3.3 d)] and , include all special characteristics in the control plan,
•comply with customer-specified definitions and symbols, and
•identify process control documents including drawings, FMEAs, control plans, and operator instructions with the customer's special characteristic symbol or the organization¡¯s equivalent symbol or notation to include those process steps that affect special characteristics.
NOTE Special characteristics can include product characteristics and process parameters.
7.3.3 Design and development outputs
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.3.3 Design and development outputs
The outputs of design and development shall be in a form suitable for verification against the design and development input and shall be approved prior to release.
Design and development outputs shall
a) meet the input requirements for design and development,
b) provide appropriate information for purchasing, production and service provision,
c) contain or reference , product acceptance criteria, and
d) specify the characteristics of the product that are essential for its safe and proper use.
NOTE Information for production and service provision can include details for the preservation of product.
7.3.3.1 Product design outputs , ¡ª Supplemental
The product design output shall be expressed in terms that can be verified and validated against product design input requirements. The product design output shall include
•design FMEA, reliability results,
•product special characteristics and specifications,
•product error-proofing, as appropriate,
•product definition including drawings or mathematically based data,
•product design reviews results, and
•diagnostic guidelines, where applicable.
7.3.3.2 Manufacturing process design output
The manufacturing process design output shall be expressed in terms that can be verified against manufacturing process design input requirements and validated. The manufacturing process design output shall include
•specifications and drawings,
•manufacturing process flow chart/layout,
•manufacturing process FMEAs,
•control plan (see 7.5.1.1),
•work instructions,
•process approval acceptance criteria,
•data for quality, reliability, maintainability and measurability,
•results of error-proofing activities, as appropriate, and
•methods of rapid detection and feedback of product/manufacturing process nonconformities.
7.3.4 Design and development review
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.3.4 Design and development review
At suitable stages, systematic reviews of design and development shall be performed in accordance with planned arrangements (see 7.3.1)
a) to evaluate the ability of the results of design and development to meet requirements, and
b) to identify any problems and propose necessary actions.
Participants in such reviews shall include representatives of functions concerned with the design and development stage(s) being reviewed. Records of the results of the reviews and any necessary actions shall be maintained (see 4.2.4).
NOTE These reviews are normally coordinated with the design phases and include manufacturing process design and development.
7.3.4.1 Monitoring
Measurements at specified stages of design and development shall be defined, analysed and reported with summary results as an input to management review.
NOTE These measurements include quality risks, costs, lead-times, critical paths and others, as appropriate.
7.3.5 Design and development verification
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.3.5 Design and development verification
Verification shall be performed in accordance with planned arrangements (see 7.3.1) to ensure that the design and development outputs have met the design and development input requirements. Records of the results of the verification and any necessary actions shall be maintained (see 4.2.4).
7.3.6 Design and development validation
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.3.6 Design and development validation
Design and development validation shall be performed in accordance with planned arrangements (see 7.3.1) to ensure that the resulting product is capable of meeting the requirements for the specified application or intended use, where known. Wherever practicable, validation shall be completed prior to the delivery or implementation of the product. Records of the results of validation and any necessary actions shall be maintained (see 4.2.4).
NOTE 1 The validation process normally includes an analysis of field reports for similar products.
NOTE 2 The requirements of 7.3.5 and 7.3.6 above apply to both product and manufacturing processes.
7.3.6.1 Design and development validation ¡ª Supplemental
Design and development validation shall be performed in accordance with customer requirements, including programme timing.
7.3.6.2 Prototype programme
When required by the customer, the organization shall have a prototype programme and control plan. The organization shall use, wherever possible, the same suppliers, tooling and manufacturing processes as will be used in production.
All performance-testing activities shall be monitored for timely completion and conformity to requirements.
While services may be outsourced, the organization shall be responsible for the outsourced services, including technical leadership.
7.3.6.3 Product approval process
The organization shall conform to a product and manufacturing process approval procedure recognized by the customer.
NOTE Product approval should be subsequent to the verification of the manufacturing process.
This product and manufacturing process approval procedure shall also be applied to suppliers.
7.3.7 Control of design and development changes
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.3.7 Control of design and development changes
Design and development changes shall be identified and records maintained. The changes shall be reviewed, verified and validated, as appropriate, and approved before implementation. The review of design and development changes shall include evaluation of the effect of the changes on constituent parts and product already delivered. Records of the results of the review of changes and any necessary actions shall be maintained (see 4.2.4).
NOTE Design and development changes include all changes during the product programme life (see 7.1.4).
7.4 Purchasing
7.4.1 Purchasing process
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.4Purchasing
7.4.1 Purchasing process
The organization shall ensure that purchased product conforms to specified purchase requirements. The type and extent of control applied to the supplier and the purchased product shall be dependent upon the
effect of the purchased product on subsequent product realization or the final product.
The organization shall evaluate and select suppliers based on their ability to supply products in accordance with the organization's requirements. Criteria for selection, evaluation, and re-evaluation shall be established. Records of the results of evaluations and any necessary actions arising from the
evaluation shall be maintained (see 4.2.4)
NOTE 1 Purchased products above include all products and services that affect customer requirements such as subassembly, sequencing, sorting, rework and calibration services.
NOTE 2 When there are mergers, acquisitions or affiliations associated with suppliers, the organization should verify the continuity of the supplier's quality management system and its effectiveness.
7.4.1.1 Statutory and regulatory conformity
All purchased products or materials used in product shall conform to applicable statutory and regulatory requirements.
7.4.1.2 Supplier quality management system development
The organization shall perform supplier quality management system development with the goal of supplier conformity with this Technical Specification. Conformity with ISO 9001:2008 is the first step in achieving this goal.
NOTE The prioritization of suppliers for development depends upon, for example, the supplier's quality performance and the importance of the product supplied.
Unless otherwise specified by the customer, suppliers to the organization shall be third party, registered to ISO 9001:2008 by an accredited third-party certification body.
7.4.1.3 Customer-approved sources
Where specified by the contract (e.g. customer engineering drawing, specification), the organization shall purchase products, materials or services from approved sources.
The use of customer-designated sources, including tool/gauge suppliers, does not relieve the organization of the responsibility for ensuring the quality of purchased products.
7.4.2 Purchasing information
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.4.2 Purchasing information
Purchasing information shall describe the product to be purchased, including, where appropriate
a) requirements for approval of product, procedures, processes and equipment,
b) requirements for qualification of personnel, and
c) quality management system requirements.
The organization shall ensure the adequacy of specified purchase requirements prior to their communication to the supplier.
7.4.3 Verification of purchased product
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.4.3 Verification of purchased product
The organization shall establish and implement the inspection or other activities necessary for ensuring that purchased product meets specified purchase requirements.
Where the organization or its customer intends to perform verification at the supplier's premises, the organization shall state the intended verification arrangements and method of product release in the purchasing information.
7.4.3.1 Incoming product conformity to requirements
The organization shall have a process to assure the quality of purchased product (see 7.4.3) utilizing one or more of the following methods:
•receipt of, and evaluation of, statistical data by the organization;
•receiving inspection and/or testing, such as sampling based on performance;
•second- or third-party assessments or audits of supplier sites, when coupled with records of acceptable delivered product conformity to requirements;
•part evaluation by a designated laboratory;
•another method agreed with the customer.
7.4.3.2 Supplier monitoring
Supplier performance shall be monitored through the following indicators:
•delivered product conformity to requirements;
•customer disruptions, including field returns;
•delivery schedule performance (including incidents of premium freight);
•special status customer notifications related to quality or delivery issues.
The organization shall promote supplier monitoring of the performance of their manufacturing processes.
7.5 Production and service provision
7.5.1 Control of production and service provision
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.5 Production and service provision
7.5.1 Control of production and service provision
The organization shall plan and carry out production and service provision under controlled
conditions. Controlled conditions shall include, as applicable,
a) the availability of information that describes the characteristics of the product,
b) the availability of work instructions, as necessary,
c) the use of suitable equipment,
d) the availability and use of monitoring and measuring equipment,
e) the implementation of monitoring and measurement, and
f) the implementation of product release, delivery and post-delivery activities.
7.5.1.1 Control plan
The organization shall
•develop control plans (see Annex A) at the system, subsystem, component and/or material level for the product supplied, including those for processes producing bulk materials as well as parts, and
•have a control plan for pre-launch and production that takes into account the design FMEA and manufacturing process FMEA outputs.
The control plan shall
•list the controls used for the manufacturing process control,
•include methods for monitoring of control exercised over special characteristics (see 7.3.2.3) defined by both the customer and the organization,
•include the customer-required information, if any, and
•initiate the specified reaction plan (see 8.2.3.1) when the process becomes unstable or not statistically capable.
Control plans shall be reviewed and updated when any change occurs affecting product, manufacturing process, measurement, logistics, supply sources or FMEA (see 7.1.4).
NOTE Customer approval may be required after review or update of the control plan.
7.5.1.2 Work instructions
The organization shall prepare documented work instructions for all employees having responsibilities for the operation of processes that impact conformity to product requirements. These instructions shall be accessible for use at the work station.
These instructions shall be derived from sources such as the quality plan, the control plan and the product realization process.
7.5.1.3 Verification of job set-ups
Job set-ups shall be verified whenever performed, such as an initial run of a job, material changeover or job change.
Work instructions shall be available for set-up personnel. The organization shall use statistical methods of verification, where applicable.
NOTE Last-off-part comparisons are recommended.
7.5.1.4 Preventive and predictive maintenance
The organization shall identify key process equipment and provide resources for machine/equipment maintenance and develop an effective planned total preventive maintenance system. As a minimum, this system shall include the following:
•planned maintenance activities;
•packaging and preservation of equipment, tooling and gauging;
•availability of replacement parts for key manufacturing equipment;
•documenting, evaluating and improving maintenance objectives.
The organization shall utilize predictive maintenance methods to continually improve the effectiveness and the efficiency of production equipment.
7.5.1.5 Management of production tooling
The organization shall provide resources for tool and gauge design, fabrication and verification activities.
The organization shall establish and implement a system for production tooling management including:
•maintenance and repair facilities and personnel;
•storage and recovery;
•set-up;
•tool-change programmes for perishable tools;
•tool design modification documentation, including engineering change level;
•tool modification and revision to documentation;
•tool identification, defining the status, such as production, repair or disposal.
The organization shall implement a system to monitor these activities if any work is outsourced.
NOTE This requirement also applies to the availability of tools for vehicle service parts.
7.5.1.6 Production scheduling
Production shall be scheduled in order to meet customer requirements, such as just-in-time supported by an information system that permits access to production information at key stages of the process and is order driven.
7.5.1.7 Feedback of information from service
A process for communication of information on service concerns to manufacturing, engineering and design activities shall be established and maintained.
NOTE The intent of the addition of ¡°service concerns¡± to this subclause is to ensure that the organization is aware of
nonconformities that occur outside of its organization.
7.5.1.8 Service agreement with customer
When there is a service agreement with the customer, the organization shall verify the effectiveness of any organization service centres, any special-purpose tools or measurement equipment, and the training of service personnel.
7.5.2 Validation of processes for production and service provision
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.5.2 Validation of processes for production and service provision
The organization shall validate any processes for production and service provision where the resulting output cannot be verified by subsequent monitoring or measurement and, as a consequence, deficiencies become apparent only after the product is in use or the service has been delivered.
Validation shall demonstrate the ability of these processes to achieve planned results.
The organization shall establish arrangements for these processes including, as applicable
a) defined criteria for review and approval of the processes,
b) approval of equipment and qualification of personnel,
c) use of specific methods and procedures,
d) requirements for records (see 4.2.4), and
e) revalidation.
7.5.2.1 Validation of processes for production and service provision ¡ª Supplemental
The requirements of 7.5.2 shall apply to all processes for production and service provision.
7.5.3 Identification and traceability
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.5.3 Identification and traceability
Where appropriate, the organization shall identify the product by suitable means throughout product realization.
The organization shall identify the product status with respect to monitoring and measurement requirements
throughout product realization.
Where traceability is a requirement, the organization shall control the unique identification of the product and maintain records (see 4.2.4).
NOTE In some industry sectors, configuration management is a means by which identification and traceability are maintained.
NOTE Inspection and test status is not indicated by the location of product in the production flow unless inherently
obvious, such as material in an automated production transfer process. Alternatives are permitted, if the status is clearly
identified, documented and achieves the designated purpose.
7.5.3.1 Identification and traceability ¡ª Supplemental
The words ¡°Where appropriate¡± in 7.5.3 shall not apply.
7.5.4 Customer property
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.5.4 Customer property
The organization shall exercise care with customer property while it is under the organization's control or being used by the organization. The organization shall identify, verify, protect and safeguard customer property provided for use or incorporation into the product. If any customer property is lost, damaged or otherwise found to be unsuitable for use, the organization shall report this to the customer and maintain records (see 4.2.4).
NOTE Customer property can include intellectual property and personal data.
NOTE Customer-owned returnable packaging is included in this subclause.
7.5.4.1 Customer-owned production tooling
Customer-owned tools, manufacturing, test, inspection tooling and equipment shall be permanently marked so that the ownership of each item is visible, and can be determined.
7.5.5 Preservation of product
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.5.5 Preservation of product
The organization shall preserve the product during internal processing and delivery to the intended destination in order to maintain conformity to requirements. As applicable, preservation shall include identification, handling, packaging, storage and protection. Preservation shall also apply to the constituent parts of a product.
7.5.5.1 Storage and inventory
In order to detect deterioration, the condition of product in stock shall be assessed at appropriate planned intervals.
The organization shall use an inventory management system to optimize inventory turns over time and assure stock rotation, such as ¡°first-in-first-out¡± (FIFO). Obsolete product shall be controlled in a similar manner to nonconforming product.
7.6 Control of monitoring and measuring equipment
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
7.6 Control of monitoring and measuring equipment
The organization shall determine the monitoring and measurement to be undertaken and the monitoring and measuring equipment needed to provide evidence of conformity of product to determined requirements.
The organization shall establish processes to ensure that monitoring and measurement can be carried out and are carried out in a manner that is consistent with the monitoring and measurement requirements.
Where necessary to ensure valid results, measuring equipment shall
a) be calibrated or verified, or both, at specified intervals, or prior to use, against measurement standards traceable to international or national measurement standards; where no such standards exist, the basis used for calibration or verification shall be recorded (see 4.2.4);
b) be adjusted or re-adjusted as necessary;
c) have identification in order to determine its calibration status;
d) be safeguarded from adjustments that would invalidate the measurement result;
e) be protected from damage and deterioration during handling, maintenance and storage.
In addition, the organization shall assess and record the validity of the previous measuring results when the equipment is found not to conform to requirements. The organization shall take appropriate action on the equipment and any product affected.
Records of the results of calibration and verification shall be maintained (see 4.2.4).
When used in the monitoring and measurement of specified requirements, the ability of computer software to satisfy the intended application shall be confirmed. This shall be undertaken prior to initial use and reconfirmed as necessary.
NOTE Confirmation of the ability of computer software to satisfy the intended application would typically include its verification and configuration management to maintain its suitability for use.
NOTE A number or other identifier traceable to the device calibration record meets the intent of requirement c) above.
7.6.1 Measurement system analysis
Statistical studies shall be conducted to analyse the variation present in the results of each type of measuring and test equipment system. This requirement shall apply to measurement systems referenced in the control plan. The analytical methods and acceptance criteria used shall conform to those in customer reference manuals on measurement systems analysis. Other analytical methods and acceptance criteria may be used if approved by the customer.
7.6.2 Calibration/verification records
Records of the calibration/verification activity for all gauges, measuring and test equipment, needed to provide evidence of conformity of product to determined requirements, including employee- and customer-owned equipment, shall include
•equipment identification, including the measurement standard against which the equipment is calibrated,
•revisions following engineering changes,
•any out-of-specification readings as received for calibration/verification,
•an assessment of the impact of out-of-specification condition,
•statements of conformity to specification after calibration/verification, and
•notification to the customer if suspect product or material has been shipped.
7.6.3 Laboratory requirements
7.6.3.1 Internal laboratory
An organization's internal laboratory facility shall have a defined scope that includes its capability to perform the required inspection, test or calibration services. This laboratory scope shall be included in the quality management system documentation. The laboratory shall specify and implement, as a minimum, technical requirements for
•adequacy of the laboratory procedures,
•competency of the laboratory personnel, testing of the product,
•capability to perform these services correctly, traceable to the relevant process standard (such as ASTM, EN, etc.), and
•review of the related records.
NOTE Accreditation to ISO/IEC 17025 may be used to demonstrate the organization's in-house laboratory conformity
to this requirement but is not mandatory.
7.6.3.2 External laboratory
External/commercial/independent laboratory facilities used for inspection, test or calibration services by the organization shall have a defined laboratory scope that includes the capability to perform the required inspection, test or calibration, and either
•there shall be evidence that the external laboratory is acceptable to the customer, or
•the laboratory shall be accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 or national equivalent.
NOTE 1 Such evidence may be demonstrated by customer assessment, for example, or by customer-approved second-party assessment that the laboratory meets the intent of ISO/IEC 17025 or national equivalent.
NOTE 2 When a qualified laboratory is not available for a given piece of equipment, calibration services may be performed by the equipment manufacturer. In such cases, the organization should ensure that the requirements listed in 7.6.3.1 have been met.
8 Measurement, analysis and improvement
8.1 General
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8 Measurement, analysis and improvement
8.1 General
The organization shall plan and implement the monitoring, measurement, analysis and improvement processes needed
a) to demonstrate conformity to product requirements,
b) to ensure conformity of the quality management system, and
c) to continually improve the effectiveness of the quality management system.
This shall include determination of applicable methods, including statistical techniques, and the extent of their use.
8.1.1 Identification of statistical tools
Appropriate statistical tools for each process shall be determined during advance quality planning and included in the control plan.
8.1.2 Knowledge of basic statistical concepts
Basic statistical concepts, such as variation, control (stability), process capability and over-adjustment shall be understood and utilized throughout the organization.
8.2 Monitoring and measurement
8.2.1 Customer satisfaction
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8.2 Monitoring and measurement
8.2.1 Customer satisfaction
As one of the measurements of the performance of the quality management system, the organization shall
monitor information relating to customer perception as to whether the organization has met customer requirements. The methods for obtaining and using this information shall be determined.
NOTE Monitoring customer perception can include obtaining input from sources such as customer satisfaction surveys, customer data on delivered product quality, user opinion surveys, lost business analysis, compliments, warranty claims and dealer reports.
NOTE Consideration should be given to both internal and external customers.
8.2.1.1 Customer satisfaction ¡ª Supplemental
Customer satisfaction with the organization shall be monitored through continual evaluation of performance of the realization processes. Performance indicators shall be based on objective data and include, but not be limited to:
•delivered part quality performance,
•customer disruptions, including field returns,
•delivery schedule performance (including incidents of premium freight), and
•customer notifications related to quality or delivery issues.
The organization shall monitor the performance of manufacturing processes to demonstrate compliance with
customer requirements for product quality and efficiency of the process.
8.2.2 Internal audit
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8.2.2 Internal audit
The organization shall conduct internal audits at planned intervals to determine whether the quality management system
a) conforms to the planned arrangements (see 7.1), to the requirements of this International Standard and to the quality management system requirements established by the organization, and
b) is effectively implemented and maintained.
An audit programme shall be planned, taking into consideration the status and importance of the processes and areas to be audited, as well as the results of previous audits. The audit criteria, scope, frequency and methods shall be defined. The selection of auditors and conduct of audits shall ensure objectivity and impartiality of the audit process. Auditors shall not audit their own work.
A documented procedure shall be established to define the responsibilities and requirements for planning and conducting audits, establishing records and reporting results.
Records of the audits and their results shall be maintained (see 4.2.4).
The management responsible for the area being audited shall ensure that any necessary corrections and corrective actions are taken without undue delay to eliminate detected nonconformities and their causes.
Follow-up activities shall include the verification of the actions taken and the reporting of verification results (see 8.5.2).
NOTE See ISO 19011 for guidance.
8.2.2.1 Quality management system audit
The organization shall audit its quality management system to verify compliance with this Technical Specification and any additional quality management system requirements.
8.2.2.2 Manufacturing process audit
The organization shall audit each manufacturing process to determine its effectiveness.
8.2.2.3 Product audit
The organization shall audit products at appropriate stages of production and delivery to verify conformity to all specified requirements, such as product dimensions, functionality, packaging and labelling, at a defined frequency.
8.2.2.4 Internal audit plans
Internal audits shall cover all quality management related processes, activities and shifts, and shall be scheduled according to an annual plan.
When internal/external nonconformities or customer complaints occur, the audit frequency shall be appropriately increased.
NOTE Specific checklists should be used for each audit.
8.2.2.5 Internal auditor qualification
The organization shall have internal auditors who are qualified to audit the requirements of this Technical Specification( see 6.2.2.2).
8.2.3 Monitoring and measurement of processes
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8.2.3 Monitoring and measurement of processes
The organization shall apply suitable methods for monitoring and, where applicable, measurement of the quality management system processes. These methods shall demonstrate the ability of the processes to achieve planned results. When planned results are not achieved, correction and corrective action shall be taken, as appropriate.
NOTE When determining suitable methods, it is advisable that the organization consider the type and extent of monitoring or measurement appropriate to each of its processes in relation to their impact on the conformity to product requirements and on the effectiveness of the quality management system.
8.2.3.1 Monitoring and measurement of manufacturing processes
The organization shall perform process studies on all new manufacturing (including assembly or sequencing) processes to verify process capability and to provide additional input for process control.
The results of process studies shall be documented with specifications, where applicable, for means of production, measurement and test, and maintenance instructions. These documents shall include objectives for manufacturing process capability, reliability, maintainability and availability, as well as acceptance criteria.
The organization shall maintain manufacturing process capability or performance as specified by the customer part approval process requirements. The organization shall ensure that the control plan and process flow diagram are implemented, including adherence to the specified
•measurement techniques,
•sampling plans,
•acceptance criteria, and
•reaction plans when acceptance criteria are not met.
Significant process events, such as tool change or machine repair, shall be recorded.
The organization shall initiate a reaction plan from the control plan for characteristics that are either not statistically capable or are unstable. These reaction plans shall include containment of product and 100 % inspection, as appropriate. A corrective action plan shall then be completed by the organization, indicating specific timing and assigned responsibilities to assure that the process becomes stable and capable. The plans shall be reviewed with and approved by the customer when so required.
The organization shall maintain records of effective dates of process changes.
8.2.4 Monitoring and measurement of product
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8.2.4 Monitoring and measurement of product
The organization shall monitor and measure the characteristics of the product to verify that product requirements have been met. This shall be carried out at appropriate stages of the product realization process in accordance with the planned arrangements (see 7.1).
Evidence of conformity with the acceptance criteria shall be maintained.
Records shall indicate the person(s) authorizing release of product for delivery to the customer (see 4.2.4).
The release of product and delivery of service to the customer shall not proceed until the planned arrangements (see 7.1) have been satisfactorily completed, unless otherwise approved by a relevant authority and, where applicable, by the customer.
NOTE When selecting product parameters to monitor compliance to specified internal and external requirements, the
organization determines the types of product characteristics, leading to
•the types of measurement,
•suitable measurement means, and
•the capability and skills required.
8.2.4.1 Layout inspection and functional testing
A layout inspection and a functional verification to applicable customer engineering material and performance standards shall be performed for each product as specified in the control plans. Results shall be available for customer review.
NOTE Layout inspection is the complete measurement of all product dimensions shown on the design records.
8.2.4.2 Appearance items
For organizations manufacturing parts designated by the customer as ¡°appearance items¡±, the organization shall provide
•appropriate resources, including lighting, for evaluation,
•masters for colour, grain, gloss, metallic brilliance, texture, distinctness of image (DOI), as appropriate,
•maintenance and control of appearance masters and evaluation equipment, and
•verification that personnel making appearance evaluations are competent and qualified to do so.
8.3 Control of nonconforming product
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8.3 Control of nonconforming product
The organization shall ensure that product which does not conform to product requirements is identified and controlled to prevent its unintended use or delivery. A documented procedure shall be established to define the controls and related responsibilities and authorities for dealing with nonconforming product.
Where applicable, the organization shall deal with nonconforming product by one or more of the following ways:
a) by taking action to eliminate the detected nonconformity;
b) by authorizing its use, release or acceptance under concession by a relevant authority and, where applicable, by the customer;
c) by taking action to preclude its original intended use or application;
d) by taking action appropriate to the effects, or potential effects, of the nonconformity when nonconforming product is detected after delivery or use has started.
When nonconforming product is corrected it shall be subject to re-verification to demonstrate conformity to the requirements.
Records of the nature of nonconformities and any subsequent actions taken, including concessions obtained, shall be maintained (see 4.2.4).
8.3.1 Control of nonconforming product ¡ª Supplemental
Product with unidentified or suspect status shall be classified as nonconforming product (see 7.5.3).
8.3.2 Control of reworked product
Instructions for rework, including re-inspection requirements, shall be accessible to and utilized by the appropriate personnel.
8.3.3 Customer information
Customers shall be informed promptly in the event that nonconforming product has been shipped.
8.3.4 Customer waiver
The organization shall obtain a customer concession or deviation permit prior to further processing whenever the product or manufacturing process is different from that which is currently approved.
The organization shall maintain a record of the expiration date or quantity authorized. The organization shall also ensure compliance with the original or superseding specifications and requirements when the authorization expires. Material shipped on an authorization shall be properly identified on each shipping container.
This applies equally to purchased product. The organization shall approve any requests from suppliers before submission to the customer.
8.4 Analysis of data
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8.4 Analysis of data
The organization shall determine, collect and analyse appropriate data to demonstrate the suitability and effectiveness of the quality management system and to evaluate where continual improvement of the effectiveness of the quality management system can be made. This shall include data generated as a result of monitoring and measurement and from other relevant sources. The analysis of data shall provide information relating to
a) customer satisfaction (see 8.2.1),
b) conformity to product requirements (see 8.2.4),
c) characteristics and trends of processes and products, including opportunities for preventive action (see 8.2.3 and 8.2.4), and
d) suppliers (see 7.4).
8.4.1 Analysis and use of data
Trends in quality and operational performance shall be compared with progress toward objectives and lead to action to support the following:
•development of priorities for prompt solutions to customer-related problems;
•determination of key customer-related trends and correlation for status review, decision-making and longer term planning;
•an information system for the timely reporting of product information arising from usage.
NOTE Data should be compared with those of competitors and/or appropriate benchmarks.
8.5 Improvement
8.5.1 Continual improvement
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8.5 Improvement
8.5 1 Continual improvement
The organization shall continually improve the effectiveness of the quality management system through the use of the quality policy, quality objectives, audit results, analysis of data, corrective and preventive actions and management review.
8.5.1.1 Continual improvement of the organization
The organization shall define a process for continual improvement.
8.5.1.2 Manufacturing process improvement
Manufacturing process improvement shall continually focus upon control and reduction of variation in product characteristics and manufacturing process parameters.
NOTE 1 Controlled characteristics are documented in the control plan.
NOTE 2 Continual improvement is implemented once manufacturing processes are capable and stable, or product characteristics are predictable and meet customer requirements.
8.5.2 Corrective action
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8.5.2 Corrective action
The organization shall take action to eliminate the causes of nonconformities in order to prevent recurrence.
Corrective actions shall be appropriate to the effects of the nonconformities encountered.
A documented procedure shall be established to define requirements for
a) reviewing nonconformities (including customer complaints),
b) determining the causes of nonconformities,
c) evaluating the need for action to ensure that nonconformities do not recur,
d) determining and implementing action needed,
e) records of the results of action taken (see 4.2.4), and
f) reviewing the effectiveness of the corrective action taken.
8.5.2.1 Problem solving
The organization shall have a defined process for problem solving leading to root cause identification and elimination.
If a customer-prescribed problem-solving format exists, the organization shall use the prescribed format.
8.5.2.2 Error-, pr, oofing
The organization shall use error-proofing methods in their corrective action process.
8.5.2.3 Corrective action impact
The organization shall apply to other similar processes and products the corrective action, and controls implemented, in order to eliminate the cause of a nonconformity.
8.5.2.4 Rejected product test/analysis
The organization shall analyse parts rejected by the customer's manufacturing plants, engineering facilities and dealerships. The organization shall minimize the cycle time of this process. Records of these analyses shall be kept and made available upon request. The organization shall perform analysis and initiate corrective action to prevent recurrence.
NOTE Cycle time related to rejected product analysis should be consistent with the determination of root cause, corrective actio, n and monitoring the effectiveness of implementation.
8.5.3 Preventive action
ISO 9001:2008, Quality management systems ¡ª Requirements
8.5.3 Preventive action
The organization shall determine action to eliminate the causes of potential nonconformities in order to prevent their occurrence. Preventive actions shall be appropriate to the effects of the potential problems.
A documented procedure shall be established to define requirements for
a) determining potential nonconformities and their causes,
b) evaluating the need for action to prevent occurrence of nonconformities,
c) determining and implementing action needed,
d) records of results of action taken (see 4.2.4), and
e) reviewing the effectiveness of the preventive action taken.
Annex A
(normative)
Control plan
A.1 Phases of the control plan
The control plan shall cover three distinct phases, as appropriate.
a) Prototype: a description of the dimensional measurements, material and performance tests that will occur during building of the prototype. The organization shall have a prototype control plan, if required by the customer.
b) Pre-launch: a description of the dimensional measurements, material and performance tests that occur after prototype and before full production. Pre-launch is defined as a production phase in the process of product realization which m, ay be required after prototype build.
c) Production: documentation of product/process characteristics, process controls, tests and measurement systems that occur during mass production.
Each part shall have a control plan but, in many cases, family control plans may cover a number of similar parts produced using a co, mmon process. Control plans are an output of the quality plan.
A.2 Elements of the control plan
The organization shall develop a control plan that includes, as a minimum, the following contents.
a) General data
•control plan number,
•issue date and revision date, if any,
•customer information (see customer requirements),
•organization's name/site designation,
•part number(s),
•part name/description,
•engineering change level,
•phase covered (prototype, pre-launch, production),
•key contact,
•part/process step number,
•process name/operation description.
b) Product control
•product-related special characteristics,
•other characteristics for control (number, product or process),
•specification/tolerance.
c) Process control
•process parameters,
•proce, ss-related special characteristics,
•machines, jigs, fixtures, tools for manufacturing.
d) Methods
•evaluation measurement technique,
•error-proofing,
•sample size and frequency,
•control method.
e) Reaction plan and corrective actions
•reaction plan (include or reference),
•corrective action.
» More Information 
